1、子类继承的方法只能操作子类继承和隐藏的成员变量名字类新定义的方法可以操作子类继承和子类新生命的成员变量,但是无法操作子类隐藏的成员变量(需要适用super关键字操作子类隐藏的成员变量。)
public class ChengYuanBianLing {
public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub CheapGoods cheap=new CheapGoods();// cheap.weight=192.32;//非法 cheap.newSetWeight(23); System.out.println(cheap.weight); System.out.println(cheap.newGetPrice()); cheap.oldSetWight(3.32); System.out.println(cheap.oldGetPrice()); }}class Goods{ public double weight; public void oldSetWight(double w){ weight=w; System.out.println("double型de weight="+weight); } public double oldGetPrice(){ double price=weight*10; return price; } }class CheapGoods extends Goods{ public int weight; public void newSetWeight(int w){ weight=w; System.out.println("新的weight="+weight); } public double newGetPrice(){ double price=weight*10; return price; } }2、方法重写 override method override
方法重写就是子类继承父类,子类方法中使用相同的方法名字和参数个数以及参数类型。子类通过重写父类的方法,可以隐藏父类的方法,重写父类的状态和行为改变为自己的状态和行为。
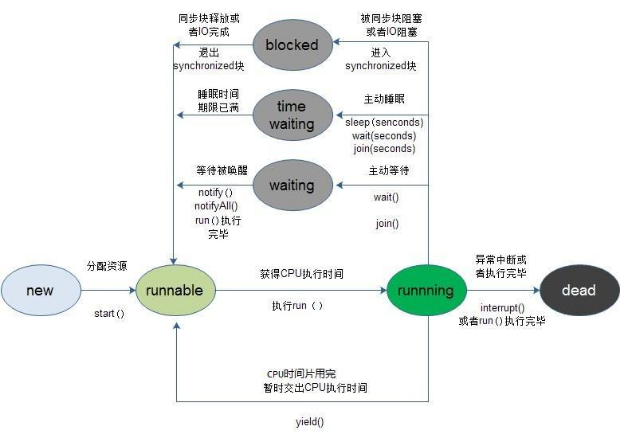
1、java线程就是一个object类,其实例继承类java.lang.Thread或其子类,创建编写线程运行时执行的代码有两种方式,一种是创建Thread子类的一个实例并重写run方法,一种是创建类的时候实现几口Runnable接口,如下展示的是run和start的区别。通过 调用start就会创建一个新的线程,但是run方法不会。run方法只会在当前的线程中运行。跟普通方法没有任何区别。
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println( "主线程ID:" +Thread.currentThread().getId()); MyThread thread1 = new MyThread( "thread1" ); thread1.start(); MyThread thread2 = new MyThread( "thread2" ); thread2.run(); } } class MyThread extends Thread{ private String name; public MyThread(String name){ this .name = name; } @Override public void run() { System.out.println( "name:" +name+ " 子线程ID:" +Thread.currentThread().getId()); } } |
运行结果:
2、线程同步问题,
public class XianChengTongBuWenTi { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Bank bank=new Bank(); bank.setMoney(300); Thread account, chsher; account=new Thread(bank); chsher=new Thread(bank); account.setName("读者"); chsher.setName("写者"); account.start(); chsher.start(); } } class Bank implements Runnable{ int money=200; public void setMoney(int n){ money=n; } public void run(){ if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("读者")) saveOrTake(200); else if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("写者")) saveOrTake(300); } public synchronized void saveOrTake(int amount){ if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("读者")){ // while(true){ for(int i=1;i<=1;i++){ money+=amount/3; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"开始工作"+"有这么多字"+amount); try{ Thread.sleep(1000); }catch(InterruptedException ex){ } } }else if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("写者")){ for(int i=1;i<=1;i++){ money+=amount/3; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"开始工作"+"有这么多字"+amount); try{ Thread.sleep(1000); }catch(InterruptedException ex){ } } } } }
3、协调线程同步问题 ,wait和notify以及notifyall是object类中的final方法,被所有的类继承且不允许重写的方法,不可以在非同步方法中使用这些关键字,
public class XieTiaoTongBu { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub TicketHouse officer=new TicketHouse(); Thread Tian, Ya; Tian=new Thread(officer); Tian.setName("田亚明"); Ya=new Thread(officer); Ya.setName("倩倩"); Tian.start(); Ya.start(); } } class TicketHouse implements Runnable{ int fiveAmount=2,tenAmount=0,twentyAmount=0; public void run(){ if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("田亚明")){ saleTicket(20); } else if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("倩倩")){ saleTicket(29); } } private synchronized void saleTicket(int money){ if(money==20){ fiveAmount+=1; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"真好合适"); } else if(money==29){ while(fiveAmount<=3){ try{ System.out.println("\n"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"等待"); wait(); }catch(InterruptedException ex){ } fiveAmount-=3; twentyAmount-=1; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } notifyAll(); } } }
4、线程联合问题 ,假设线程A在运行期间联合线程B,那么A线程会立刻终止,一直到B线程执行完毕之后A线程才会再一次排队等候CPU资源,以便恢复运行,但是如果A准备连联合的B线程已经结束,那么B.join()不会产生生活效果。